
Astronomical guide for September
September arrives loaded with shows in the night sky, with Full Moon, planetary alignments, conjunctionsand one of the best meteor showers of the year. If you are a lover of the sky, be prepared to get up early or stay up late: this month, looking up will be very worthwhile.
September 1 - Aurígidas and Venus in the Manger
- Aurigid meteor showerup to 10 per hour, fast and bright, with radiant in the constellation Auriga, near the star Capella.(Council): lie down facing northeast and enjoy the view without binoculars or telescope.
- Venus in the Manger cluster (M44, in Cancer)with binoculars, a unique spectacle, dozens of stars together in the form of a swarm.

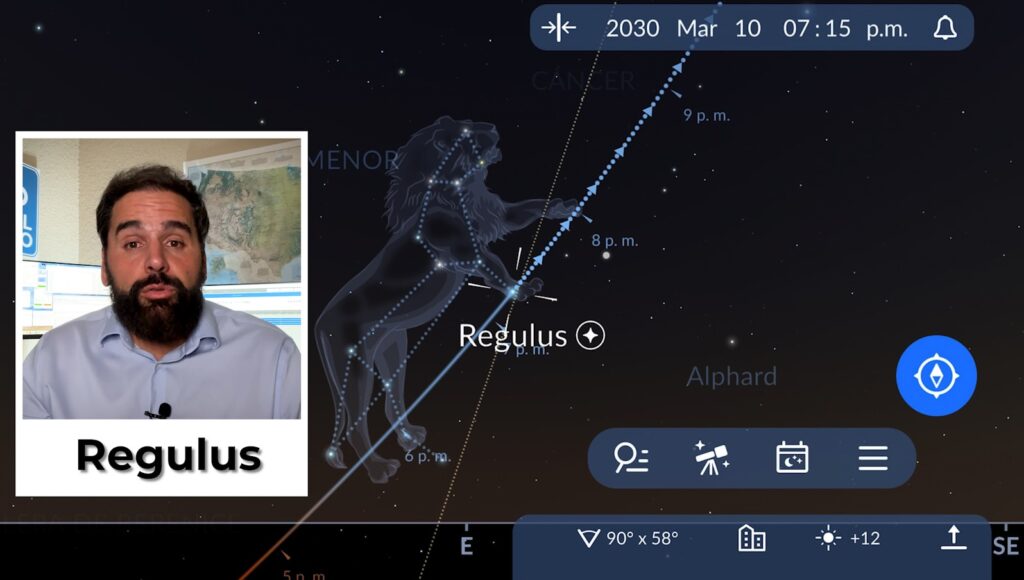
September 2 - Mercury and Regulus
- Mercuryfleeting, fleeting, approaches Régulothe "heart of the Lion". Regulus is a blue-white star, 150 times more luminous than the Sun, and actually a quadruple system.
- Of great cultural importance: its name comes from Latin Regulus ("little king") and in Arabic it was Qalb al-AsadThe "heart of the lion".
September 6 - Uranus retrograde
- Uranus begins retrograde in Taurus. With binoculars it appears greenish.
- It was the first planet discovered with telescope in 1781 by William Herschel, who initially thought it was a comet.
On the night of March 13, 1781William Herschel, a German musician who settled in England and had a passion for astronomy, pointed one of the powerful telescopes he made himself at the constellation Gemini. Among the usual stars, he was struck by a point of light that did not shine like the others: it showed a small disk, as if it were a closer object. Intrigued, he continued to observe it for several nights and found that this "curious star" moved in relation to the stellar background. This meant that it was not a fixed star, but a body of the solar system.
Important points
- September 1 - Aurígidas and Venus in the Manger
- September 2 - Mercury and Regulus
- September 6 - Uranus retrograde
- September 7 - Full Moon and Total Eclipse 🌟
- September 8 - Moon with Saturn and Neptune
- September 9th - Epsilon Perseids
- September 12 - Occultation of the Pleiades 🌟
- September 13 - Mars and Spike
- September 14 - Waning Quarter
- September 16 and 17 - Lunar Encounters
- September 19 - Venus, the Moon and Regulus 🌟
- September 21 - Triple astronomical day 🌟
- September 22nd - Autumnal Equinox
- September 24 - Moon and Mars
- September 27 - Sextants and Antares
- September 29th - Crescent Quarter
- Conclusion
At first he thought it was a comet, but the orbital calculations revealed something surprising: its trajectory was not elongated, but practically circular. It was an unknown planet, the first ever discovered with a telescope. Herschel wanted to name it Georgium Sidus in honor of King George III, although eventually the scientific community adopted the name of UranusHerschel, the Greek god of the sky, following the mythological tradition of Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. With this finding, Herschel expanded the known limits of the solar system and opened the door to modern astronomy.

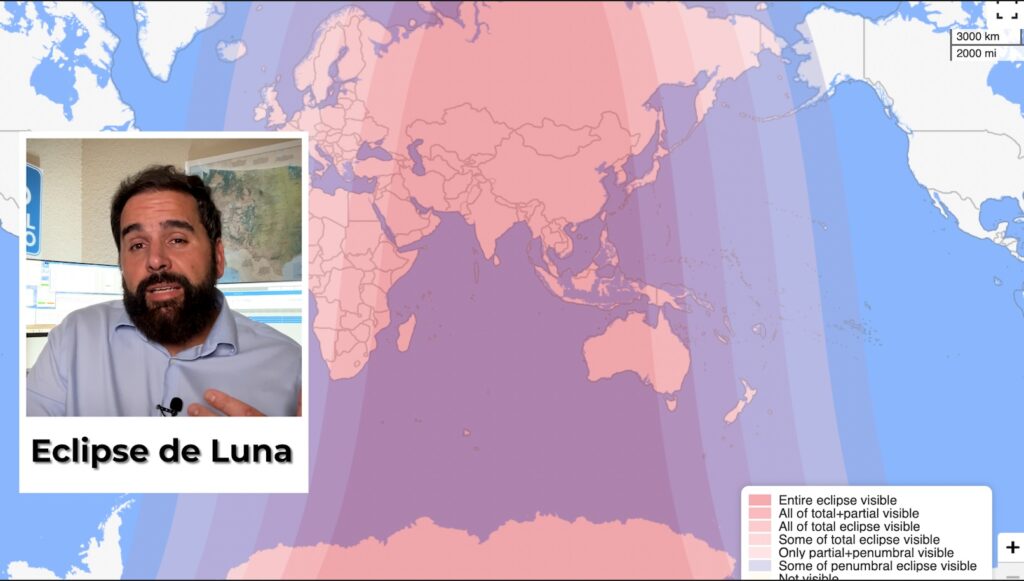
September 7 - Full Moon and Total Eclipse 🌟
- 🌕 Full Moon in Aquariusknown as the "Corn Moon" because it coincides with the harvest season.
- Total lunar eclipseBetween 17:30 and 18:53 UTC, the Moon will turn bright red (Blood Moon). Visible in Europe, Africa, Asia and Oceania.(Council)The naked eye is unforgettable, but with binoculars you can make out details in craters and lunar seas.
A total lunar eclipse occurs when our satellite enters completely into the shadow cast by the Earth. Unlike solar eclipses, it is visible from the entire hemisphere where the Moon is above the horizon. During totality, the Moon does not disappear, but rather takes on a deep reddish hue, a phenomenon known as a "Blood Moon"caused by the scattering of sunlight in the Earth's atmosphere: the blue rays are filtered and the red light is bent, staining the lunar disk. This spectacle can last more than an hour and does not require eye protection, although with binoculars or a telescope you can better appreciate the details and nuances on its surface.
September 8 - Moon with Saturn and Neptune
- The Moon approaches Saturn (golden) and to Neptune (bluish).(Council)With a telescope you will be able to see Saturn's rings almost edge-on and Neptune as a small blue disk.
September 9th - Epsilon Perseids
- Modest meteor shower (≈5/h) with radiant in Perseus.
- Related to the Swift-Tuttle comet. They are fast and bright meteors.
- In mythology, Perseus is the hero who defeated Medusa and appears together with Andromeda and Cetus in the sky.
September 12 - Occultation of the Pleiades 🌟
- The Moon will obscure the Pleiades cluster ("the Seven Sisters").
- Loaded with universal mythology: from Greece to Japan (Subaru) and Mayan cultures.(Council)The stars can be seen disappearing one by one behind the lunar disk with binoculars.
September 13 - Mars and Spike
- Reddish Mars together with Spica (Spica)the bluish star of Virgo.
- Espiga is a binary system 12,000 times more luminous than the Sun and with a surface temperature of more than 20,000 °C.
September 14 - Waning Quarter
- The Moon enters Waning Quartershowing the left half illuminated.
- Ideal for observing craters with elongated shadows near the terminator.
September 16 and 17 - Lunar Encounters
- September 16: the Moon is approaching Jupiter (its Galilean moons visible with a small telescope).
- September 17The Moon passes close to the cluster of the Nativity again.
September 19 - Venus, the Moon and Regulus 🌟
- The fine Crescent moon forms a triangle with Venus and Regulus.
- In parts of Europe and Africa, the Moon will occult Venus, a very rare event.
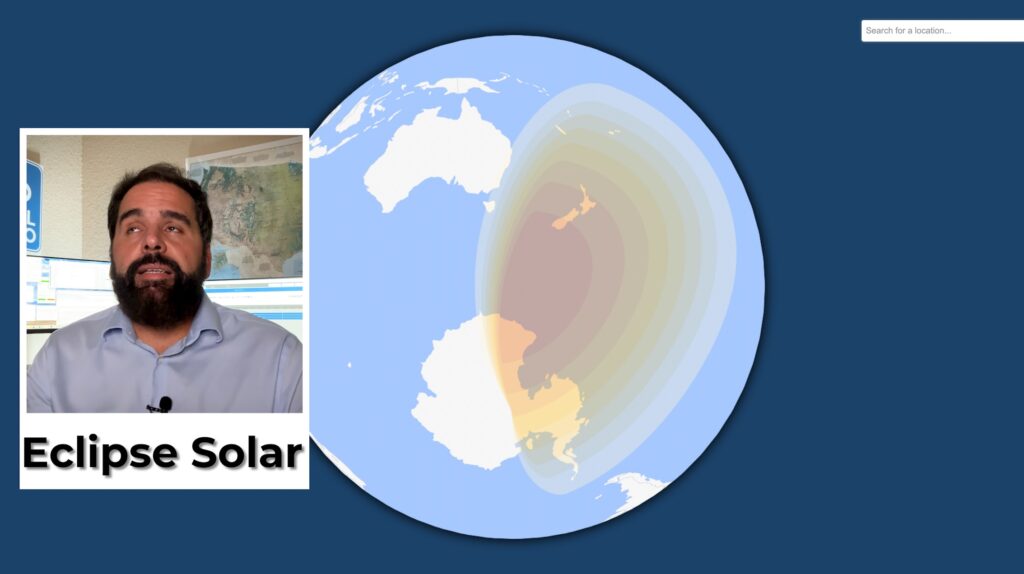
September 21 - Triple astronomical day 🌟
- Saturn in oppositionvisible all night in Pisces, with Titan (its largest moon).
- Partial solar eclipsevisible in Oceania and Antarctica (always use filters).
- 🌑 New MoonThe best night to observe the Milky Way and galaxies such as Andromeda.
September 22nd - Autumnal Equinox
- Day and night almost the same: beginning of autumn in the northern hemisphere and spring in the south.
- At Chichén Itzá, the "feathered serpent" phenomenon is projected onto the pyramid by sunlight.
The autumnal equinox occurs when the Sun crosses the celestial equator and its rays strike the Earth perpendicularly, which causes day and night to have practically the same length throughout the planet. This astronomical phenomenon marks the beginning of autumn in the northern hemisphere and spring in the southern hemisphere, and is related to the tilt of the Earth's axis (23.5°), which is responsible for the seasons. From this moment on, in the northern hemisphere the days begin to shorten and the nights to lengthen until the winter solstice, while in the southern hemisphere the opposite happens, giving way to longer and brighter days.
September 24 - Moon and Mars
- New rapprochement between the Moon and Mars in Virgoexcellent for astronomical photography.
September 27 - Sextants and Antares
- Sextant: very weak meteor shower (≈5/h), difficult to observe because of its proximity to the Sun.
- The Luna will hide AntaresScorpio's red giant. If it were in place of the Sun, its size would reach beyond that of Mars.

September 29th - Crescent Quarter
- The Moon enters the Crescent Quarterilluminating its right half.
- Excellent phase for telescopes: craters such as Copernicus and the Apennine Mountains stand out.
Conclusion
September 2025 is a stellar month for astronomy lovers. Alignments, conjunctions and meteor showers remind us that the universe is in constant motion. If you have clear skies and a little patience, every early morning will be an opportunity to marvel.
📸 Did you capture something with your camera? Tag @canalmeteo or use the hashtag. #CieloCanalMeteo so that we can share it.






