Chapter 08 - The hurricane path cone
All about hurricane season
Have you ever boarded an airplane and suddenly it shakes so much that you can't let go of the armrest? This is how it starts Atmospheric Turbulencethe new Canal Meteo podcast hosted by meteorologist and geographer Albert MartinezThe program, which invites us to discover the best kept secrets of meteorology, with a special focus on hurricanes.
Important points
In this episode:
- 01:30 Who moves the hurricanes?
- 04:40 How fast does a hurricane go?
- 06:00 Hurricanes slow down
- 10:20 Colon's first hurricane
- 13:40 The trajectory cone
- 16:30 The trajectory cone error
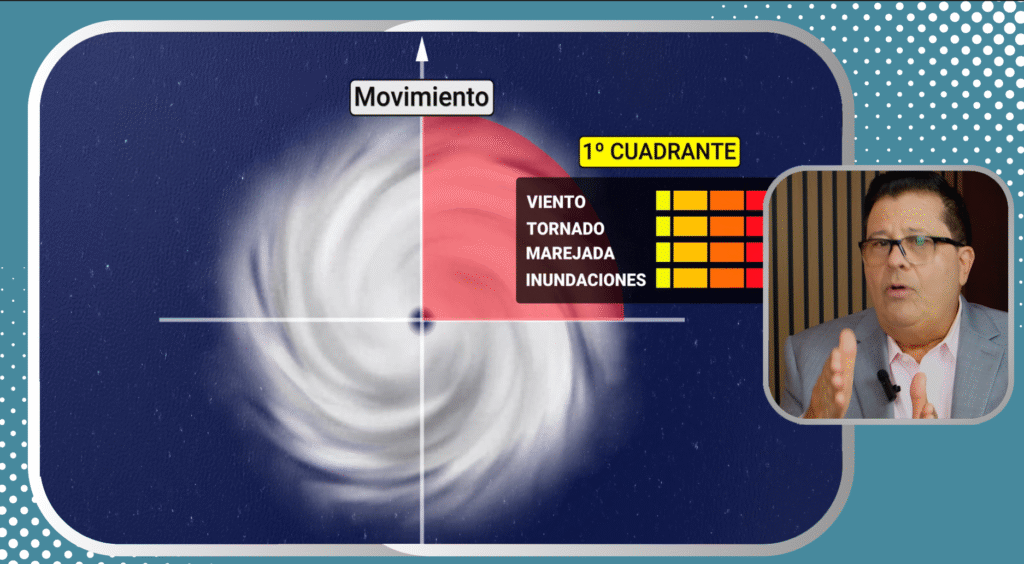
- 17:50 The wind field
- 20:00 Hurricane quadrants
- 22:50 Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic
- 26:30 Hurricane feeder bands
- 28:20 Tornadoes during a hurricane
How does a hurricane move?
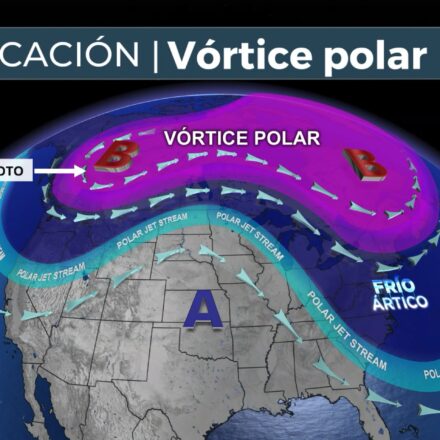
Hurricanes move mainly driven by the wind, but they are also driven by the large-scale winds which dominate the middle and upper layers of the atmosphere. In the Atlantic, the trade winds push the storms west-northwestward from their formation near the equator, keeping them within the subtropical high pressure current (Bermuda) . As they move toward higher latitudes, they come into contact with westerly winds and low pressure troughs, causing them to curve to the north and then to the northeastfollowing a hook-shaped pattern typical in the path of hurricanes. In addition, the beta effectwhich arises from the variation of the Coriolis force with latitude, generates an additional northwesterly drift in the northern hemisphere, even without strong ambient winds.
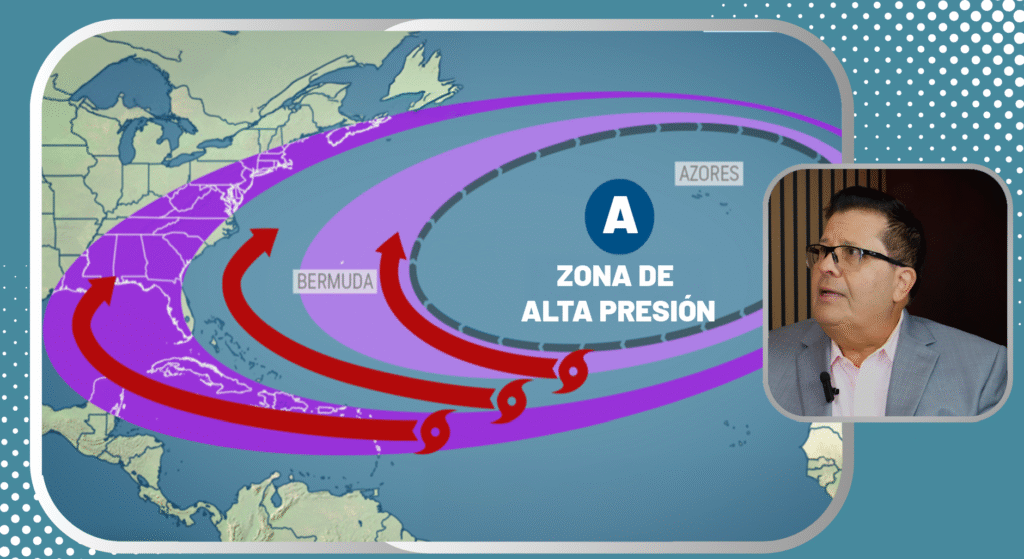
When a hurricane arrives at mid-latitudes, it may interact with the jet streamThis accelerates its northward or northeasterly movement, and it can become an extratropical cyclone if it encounters colder waters and strong currents aloft. This change usually increases its forward speed. However, if it stays in an area of weak winds-for example, in the center of persistent high pressure-it can slowing down, stopping or moving erratically . In summary, the motion of hurricanes is comparable to that of a leaf sailing down a river of air, moving according to the dominant flow of the atmosphere, and modulated by the Earth's rotation and other local forces.
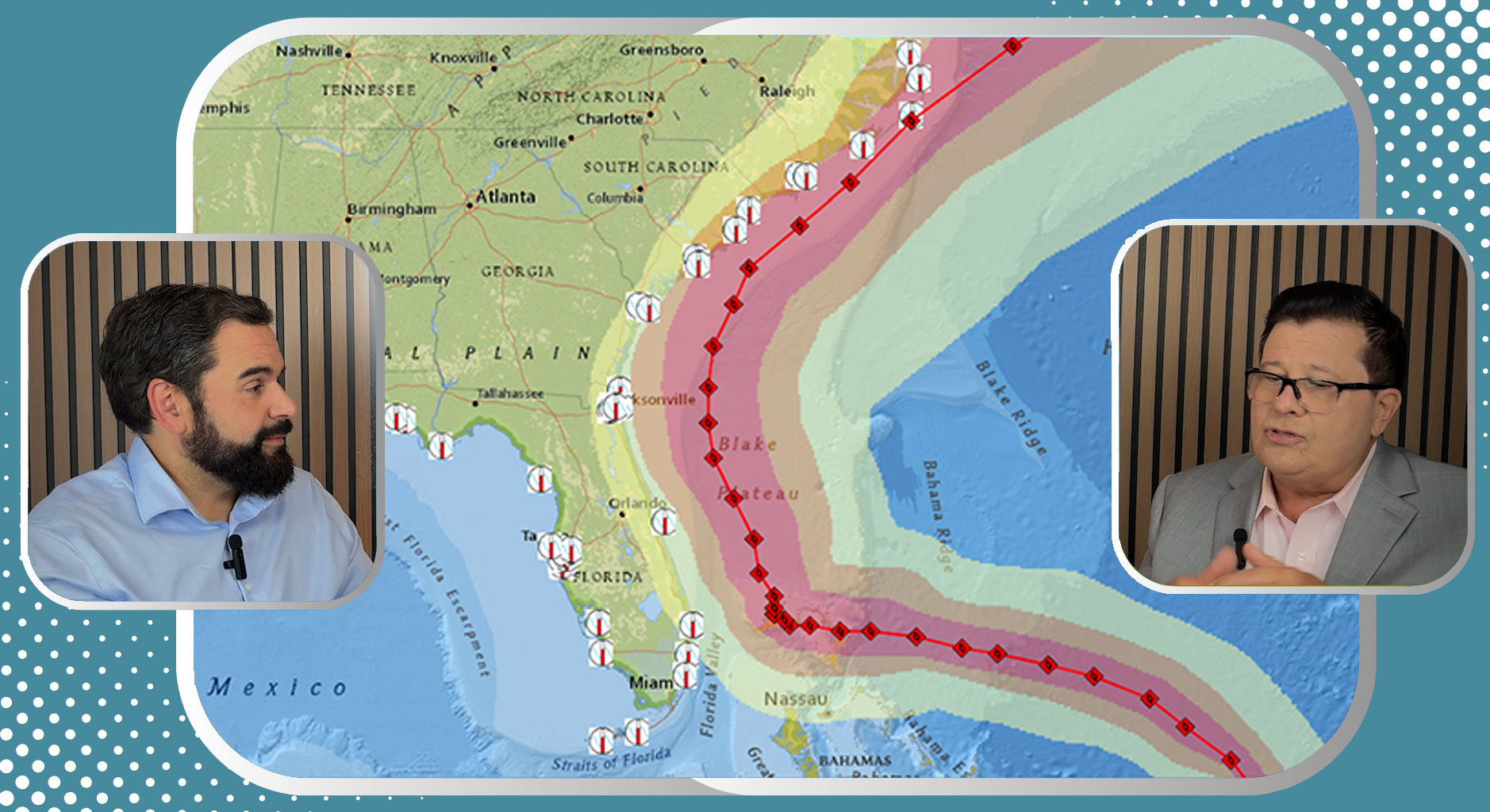
The trajectory cone
The trajectory cone (known in English as forecast cone) is a graphical tool used by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) to display the probable path of the center of a tropical cyclone during the next few days. It does not represent the size of the hurricane or its impact areas, but rather an estimate of where the eye of the hurricane could be at each time interval. It is intended to help the public and authorities visualize the uncertainty of the cyclone movement forecast.
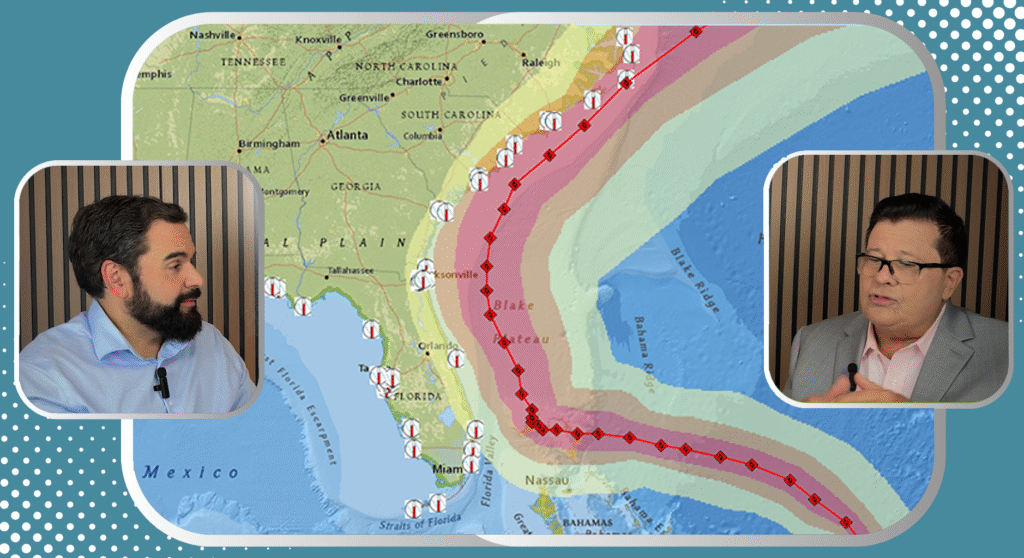
How is it calculated?
The cone is constructed from the mean forecast errors from the NHC for the last five years. For each time interval - 12, 24, 36, 36, 48, 72, 96 and 120 hours - a circle is drawn around the forecast points, the radius of which depends on the historical mean error. These circles are then smoothly connected to form the cone. Thus, the farther out the forecast horizon is, the wider the conereflecting greater uncertainty. If a hurricane deviates greatly from typical paths, it could move out of the cone, although this is not frequent.
How often is it updated and how many hours does it take?
The trajectory cone is updated four times a day with every full NHC advisory: at 5 AM, 11 AM, 5 PM and 11 PM Eastern Standard Time (ET). Each update is based on the latest models and satellite, radar and reconnaissance aircraft observations. Currently, the cone covers up to 120 hours (5 days) from the time the forecast is issued. In some particularly intense cyclones or when a prolonged impact is expected, the following may also be issued extended projectionsbut the official cone is up to 120 hours.
🏛️ Foundation of Santo Domingo
Santo Domingo, the capital of the Dominican Republicis the oldest European city founded permanently in the Americas. It was originally established on August 5, 1498 by Bartholomew ColumbusChristopher Columbus' brother, on the eastern bank of the Ozama River. However, after it was destroyed by a hurricane in 1502, the governor at the time Nicolás de Ovando rebuilt it in its present location on the western bank of the river, the July 5, 1502. Since then, it has been a key point in the history of the continent, known as the "First City of the New World".
Santo Domingo is recognized for its Colonial Zonedeclared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1990. There you can find the first European buildings in Americaas the First Cathedral of America (the Primate Cathedral of America), the Columbus Alcazar and the Ozama Fortress. It is also a cultural, economic and political center of the country, with a vibrant urban life, historic universities, museums, and a coastline bathed by the Caribbean Sea. In addition, its history is deeply linked to the development of the Spanish language, the Catholic religion and the colonization of the continent.
🎧 First audio episode now available at buzzsprout.
Follow us on social networks: @AlbertElTiempo | @CanalMeteo